Amazon Launches LEO Internet: Satellite internet has revolutionized connectivity, especially for millions living in rural and remote areas where traditional internet infrastructure fails. For years, Starlink, the SpaceX satellite internet provider, held an uncontested lead with thousands of satellites delivering broadband worldwide. But the game is changing rapidly. In 2025, Amazon launched “Amazon Leo,” its own low Earth orbit (LEO) satellite internet service, poised to rival Starlink and reshape the digital landscape. This comprehensive article breaks down Amazon Leo’s emergence, explores its technology and market impact, compares it to Starlink, and offers insights for consumers and businesses alike—with clarity and authority accessible even to a 10-year-old.
Amazon Launches LEO Internet
Amazon Leo marks a major turning point in satellite internet, combining Amazon’s technical prowess, manufacturing scale, and vast cloud ecosystem to challenge Starlink’s domain. Its rapid satellite deployment, multi-tiered user options, and enterprise focus promise more reliable, faster internet even in spots where traditional broadband struggles. For consumers and businesses eager for better connectivity, Amazon Leo’s rollout will bring fresh choices and innovations, reshaping how the digital divide gets bridged worldwide.
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Service Name | Amazon Leo (formerly Project Kuiper) |
| Satellites in Orbit | 150+ LEO satellites deployed |
| Target Markets | Residential users, enterprises, underserved & remote locations |
| Competitor | SpaceX Starlink (approx. 8,000+ satellites, millions of users) |
| Peak Internet Speed | Up to 1 Gbps planned |
| Commercial Strategy | Shift from affordability focus to enterprise and broad consumer markets |
| Official Website | Amazon Leo’s Official Page |
What Exactly Is Amazon Leo?
Amazon Leo represents Amazon’s ambitious low Earth orbit satellite internet network designed to provide blazing-fast, dependable internet to places that often struggle with traditional connectivity. The project began as Project Kuiper in 2019 with the goal to bridge the digital divide by targeting underserved regions, but recently underwent rebranding to Amazon Leo to emphasize its LEO spacecraft and sharpen its market focus.
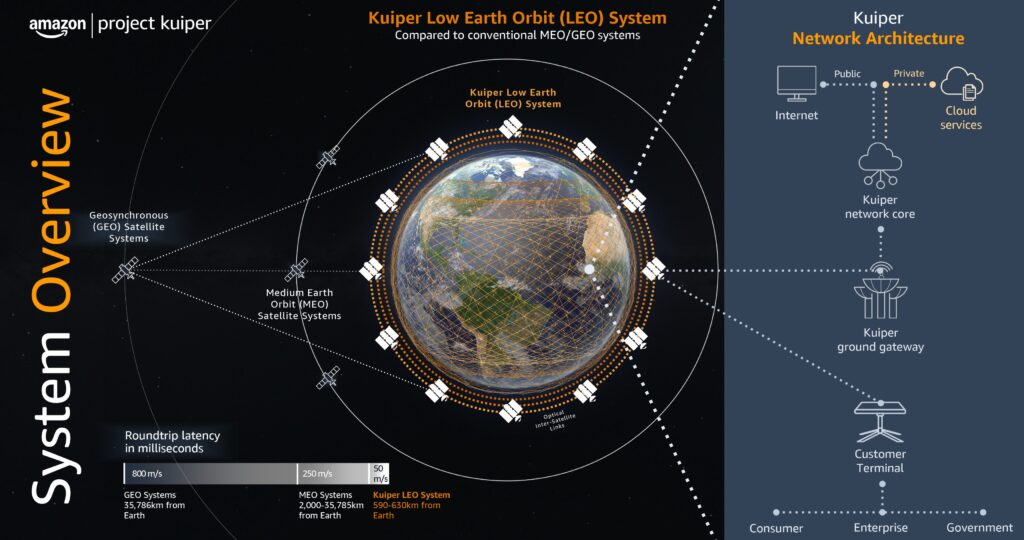
Amazon Leo satellites orbit between 590 and 630 kilometers above Earth—much closer than older geostationary satellites orbiting near 36,000 kilometers. This proximity drastically reduces signal travel time (latency), ensuring smoother internet experiences.
The rebrand coincides with a shift from emphasizing affordability and emergency access toward competing directly with Starlink for consumer, business, and enterprise broadband customers globally.
Amazon leverages its massive cloud computing ecosystem (AWS) and extensive logistics network to build and distribute this satellite constellation rapidly, showing serious intent to disrupt the satellite internet market.
Why Amazon Launches LEO Internet Matters: Breaking Down the Impact
Filling Digital Gaps Near and Far
Even near major cities, connectivity can falter due to infrastructure cost, geography, or low population density. Amazon Leo aims to fill these coverage gaps where installing ground-based fiber-optic or wireless infrastructure is cost prohibitive or physically challenging.
Pushing Innovation and Competition
Starlink paved the way by launching thousands of satellites and attracting millions of customers. Amazon Leo’s entry promises healthy competition—leading to faster innovation, better service quality, and potentially lower prices as both giants battle for supremacy.
Strategic Business Focus
Amazon is actively courting enterprise clients including airlines, shipping companies, governments, and rural businesses, offering scalable, reliable broadband solutions suited for industries requiring solid connectivity no matter location.
Leveraging Manufacturing and Launch Scale
Amazon operates a satellite manufacturing facility capable of producing up to five satellites daily, ensuring rapid replenishment and expansion of its network. The company also has over 80 launch contracts with SpaceX, Blue Origin, and others, guaranteeing a steady cadence of launches to maintain robust global coverage.
How Amazon Launches LEO Internet Works: The Technology Behind the Service
Amazon Leo’s satellite internet network consists of three core components working in seamless coordination to deliver service:
1. Satellites in Low Earth Orbit
Over 150 satellites currently form Amazon Leo’s constellation orbiting 590-630 kilometers above Earth. Flying lower than traditional satellites means lower latency (20-40 milliseconds), better speeds, and improved reliability for latency-sensitive uses like video conferencing, gaming, and streaming.
Each satellite communicates with ground stations and other satellites using advanced optical inter-satellite links (OISL)—infrared laser connections capable of data transfer at up to 100 Gbps over distances up to 2,600 kilometers—forming a fast, resilient mesh network in space.
2. Ground Infrastructure
Amazon’s ground network includes gateway antennas that transmit data to/from satellites and telemetry antennas for tracking and controlling the satellite fleet. These gateways link the satellite network to the internet, cloud services, or private networks.
3. Customer Terminals
Amazon provides three user terminal options tailored for different needs:
- Leo Nano: Compact 7×7 inch antenna delivering up to 100 Mbps for casual home users.
- Leo Pro: Slightly larger 11×11 inch model offering up to 400 Mbps for small businesses and medium workloads.
- Leo Ultra: Enterprise-grade antenna powering up to 1 Gbps speeds for data-intensive industries.
These integrated antennas combine tracking, processing, and communication hardware in sleek, user-friendly designs optimized for various environments.
Amazon Leo Service Plans: Tailored for Every Need
Amazon Leo aims to satisfy a spectrum of customers—from light internet users to hardcore data consumers and enterprises. The three-tier antenna and speed structure allow personalized connectivity:
- Leo Nano for occasional browsing, email, and streaming standard-definition video.
- Leo Pro suits businesses needing stable video conferencing, cloud computing, or heavy browsing.
- Leo Ultra targets enterprises, airports, airlines, and remote offices demanding up to gigabit connection speeds.
Tailored pricing and service agreements will accommodate casual users through large clients, further growing Amazon’s presence in the satellite internet space.
Business Partnerships and Launch Strategy: Powering the Network

Amazon has made strategic partnerships with launch providers including SpaceX, Blue Origin, United Launch Alliance, and Arianespace to ensure multiple launches per year.
Satellite assembly and final checks are conducted at Amazon’s state-of-the-art facility near Kennedy Space Center in Florida, guaranteeing quality control ahead of launches. This efficient production and launch pipeline is critical for scaling from hundreds to thousands of satellites in orbit, ensuring coverage density—and network resilience.
Additionally, Amazon collaborates with enterprises like airlines (JetBlue), defense companies (L3Harris), and broadband providers globally (NTT Docomo, Vodafone, NBN Co.) to embed Amazon Leo technology into diverse applications.
Comparing Amazon Leo and Starlink: A Side-by-Side Look
| Feature | Amazon Leo | Starlink |
|---|---|---|
| Satellites Deployed | 150+ (planned 3,236 total) | 8,000+ deployed |
| Orbit Altitude | 590-630 km | 340-1,200 km |
| Target Markets | Enterprise, home users, underserved areas | Home users, enterprise, rural communities |
| Internet Speed | 100 Mbps (Nano), 400 Mbps (Pro), 1 Gbps (Ultra) | 25 Mbps–1 Gbps, varying by region and plan |
| Latency | ~20-40 ms | ~20-40 ms |
| Pricing | Not public yet; focuses on enterprise scale | ~$110/month for residential users |
| Launch Partners | SpaceX, Blue Origin, ULA, Arianespace | SpaceX |
| Cloud Integration | Deep integration with AWS | Limited cloud integration |
Amazon Leo’s Internet integration with Amazon Web Services (AWS) creates unique synergy for enterprises using cloud, enabling seamless hybrid satellite-cloud systems. Starlink offers mobility solutions and broad consumer access, remaining strong in the consumer market.
Consumer and Business Impact of Amazon Launches LEO Internet: What to Expect
For everyday users and businesses, Amazon Leo Internet promises to:
- Expand connectivity to remote or underserved locations where internet options are limited.
- Offer reliable broadband for rural homes, remote schools, offshore platforms, and field offices.
- Improve applications requiring low latency like telehealth, remote work, video collaboration, and online gaming.
- Provide enterprise customers stable, scalable solutions for fleets, shipping, airlines, and government projects.
With Amazon’s deep pockets and operational scale, users can anticipate accelerated deployment, expanded coverage, and options to suit various needs.
Challenges and Considerations in the Satellite Internet Race
While satellite internet promises great things, there are hurdles:
- Space Debris and Sustainability: Increased satellite launches raise space debris risks. Amazon has committed to reliable deorbiting and collision avoidance.
- Regulatory Complexity: Securing satellite spectrum licenses and operating across countries’ regulatory frameworks is complex.
- Hardware Costs: Despite advancements, satellite terminals remain expensive relative to traditional broadband hardware.
- Integration with Terrestrial Networks: Combining satellite and ground internet requires seamless technical integration to avoid service gaps.
- Competition and Market Dynamics: As the industry heats up, prices, quality, and service offerings will fluctuate.